- Shanghai Zhongshen International Trade Co., Ltd. - Two decades of trade agency expertise.
- Service Hotline: 139 1787 2118
Today, with the increasing globalization, the automotive industry has become more diversified and competitive. Especially in the automotive market like Japan, the introduction of foreign automakers products has become an important issue. This article will deeply explore the entry forms of foreign automotive products in the Japanese market, the characteristics of Japans automotive access system, and tariff policies from three aspects, aiming to provide a comprehensive market analysis and business strategy suggestions.
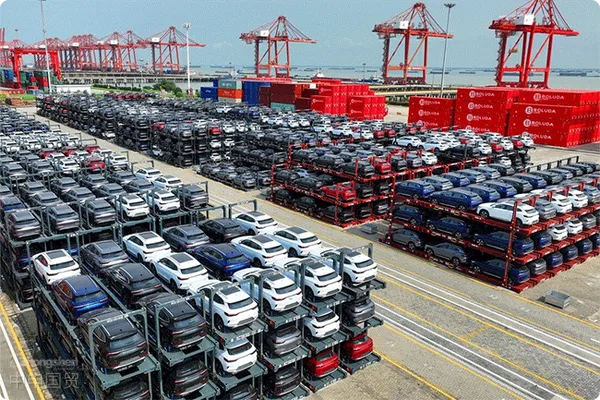

I. Entry forms of foreign automotive products
Regular import
Regular import is a common way for foreign automakers products to enter the Japanese market. Foreign automakers directly export in their own names, and directly sell their brand cars by setting up direct - selling stores or signing agency stores in Japan. This method requires automakers to establish local legal entities in Japan, which are responsible for the market access work in Japan to ensure that products meet various standards and regulations in Japan.
Parallel import
Different from regular import, parallel import is a way for Japanese parallel importers to import and sell cars in Japan through sea.foreign tradeParallel importers usually have no direct contractual relationship with foreign automakers. Parallel - imported cars can be either new or used. This method can save cumbersome certification procedures. Automakers do not need to directly participate in the certification application, and only need to cooperate with parallel importers to provide certificates and test result sheets indicating that some environmental protection and safety items of the imported models meet Japanese technical standards. Since parallel - imported cars do not need to pass the certification review of the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism of Japan, and the relevant procedures are handled by local transport branches under the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism of Japan, it is also called non - regular import.
II. Legal basis of Japanese automotive regulations
Japanese automotive - related laws aim to ensure traffic safety, prevent public hazards, ensure the relief of traffic accident victims, and effectively utilize resources. The Road Transport Vehicle Law is the legal basis for Japans automotive certification system. It not only stipulates the certification requirements before the market access of automotive products but also involves matters such as vehicle registration, annual inspection, maintenance, recycling, and penalties. The Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism of Japan has issued a series of relevant provincial decrees, announcements, circulars, etc., clarifying the specific technical requirements, test methods, and certification implementation processes of safety standards.
III. Characteristics of Japans automotive access system
High government participation
In Japan, all implementation links of automotive access certification are carried out by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism and its subordinate administrative legal person institutions. The management department is single, and the government participation is high. This also means that automakers entering the Japanese market need to communicate and coordinate more with government departments to ensure the smooth entry of products.
Few certification service institutions
Since the certification institutions have a government background, they do not conduct external publicity or provide value - added services. Automakers entering the Japanese market are relatively strong in strength, and almost all have established local legal person companies, which can uniformly manage certification, sales, after - sales, and other matters, and have few demands for certification entrustment. Therefore, internationally renowned certification institutions such as SGS and TUV have relatively little business volume in the Japanese market.
Relatively low access threshold
The standard regulations adopted in Japans automotive access certification are not higher than international standards or European standards. Overall, the regulatory requirements are not high. A large number of ECE regulations are equivalently adopted in the certification process. The number of Japans own unique standards is small, and most of them are non - major safety and environmental protection items. In addition, since the certification process is non - commercial operation, the certification cost is lower than that in China or European countries.
IV. Tariff policies
Japan is one of the few countries in the world that implement zero - tariff on automotive products, and its automotive industry has a high degree of openness. This provides favorable conditions for foreign automakers to enter the Japanese market, reduces import costs, and increases market competitiveness. However, the zero - tariff policy also means that the competition between domestic and foreign automakers in the Japanese market will be more intense. Foreign automakers need to continuously improve product quality and brand influence to gain a foothold in the Japanese market.
Related Recommendations
? 2025. All Rights Reserved. 滬ICP備2023007705號(hào)-2  PSB Record: Shanghai No.31011502009912
PSB Record: Shanghai No.31011502009912